貨號
產品規格
售價
備注
BN40885R-100ul
100ul
¥2470.00
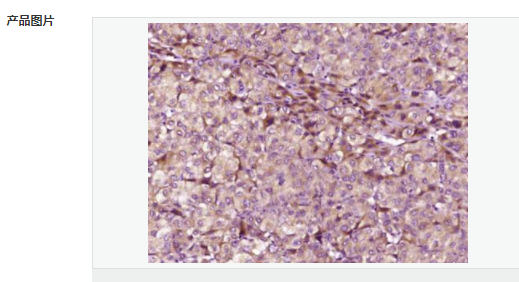
交叉反應:Human 推薦應用:IHC-P,IHC-F,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產品描述
| 英文名稱 | phospho-IKK gamma (Ser31) |
| 中文名稱 | 磷酸化KB抑制蛋白激酶γ抗體 |
| 別 名 | IKK gamma (phospho S31); p-IKK gamma (phospho S31); IkB kinase associated protein 1; IkB kinase subunit gamma; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit gamma; AMCBX1; FIP 3; FIP3; Fip3p; I kappa B kinase gamma; IkB kinase associated protein 1; IkB kinase gamma subunit; IkB kinase subunit gamma; IKBKG; IKKAP 1; IKKAP1; IKKG; IKKgamma; IKK gamma. |
| 產品類型 | 磷酸化抗體 |
| 研究領域 | 腫瘤 免疫學 信號轉導 生長因子和激素 轉錄調節因子 激酶和磷酸酶 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應 | Human, |
| 產品應用 | ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 46kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 細胞核 細胞漿 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human IKK gamma around the phosphorylation site of Ser31:EE(p-S)PL |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產品介紹 | Pro inflammatory cytokines activate the transcription factor NF kappa B by stimulating the activity of a protein kinase that phosphorylates Ikappa B, an inhibitor of NF kappa B, at sites that trigger its ubiquitination and degradation. A large, cytokine responsive Ikappa B kinase (IKK) complex has been purified and the genes encoding 2 of its subunits have been cloned. These subunits, IKK alpha and Ikk beta, are protein kinases whose function is needed for NF kappa B activation by pro inflammatory stimuli. IKK is composed of similar amounts of IKK alpha, Ikk beta, which are differentially processed forms of a third subunit, IKK gamma. IKK gamma interacts preferentially with IKK beta and is required for the activation of the IKK complex. Function: Regulatory subunit of the IKK core complex which phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B thus leading to the dissociation of the inhibitor/NF-kappa-B complex and ultimately the degradation of the inhibitor. Its binding to scaffolding polyubiquitin seems to play a role in IKK activation by multiple signaling receptor pathways. Also considered to be a mediator for TAX activation of NF-kappa-B. Could be implicated in NF-kappa-B-mediated protection from cytokine toxicity. Involved in TLR3- and IFIH1-mediated antiviral innate response; this function requires 'Lys-27'-linked polyubiquitination. Subunit: Homodimer; disulfide-linked. Component of the I-kappa-B-kinase (IKK) core complex consisting of CHUK, IKBKB and IKBKG; probably four alpha/CHUK-beta/IKBKB dimers are associated with four gamma/IKBKG subunits. The IKK core complex seems to associate with regulatory or adapter proteins to form a IKK-signalosome holo-complex. The IKK complex associates with TERF2IP/RAP1, leading to promote IKK-mediated phosphorylation of RELA/p65. Part of a complex composed of NCOA2, NCOA3, CHUK/IKKA, IKBKB, IKBKG and CREBBP. Interacts with COPS3, CYLD, NALP2, TRPC4AP and LRDD. Interacts with ATM; the complex is exported from the nucleus. Interacts with TRAF6. Interacts with HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein; the interaction activates IKBKG. Interacts with TANK; the interaction is enhanced by IKBKE and TBK1. Part of a ternary complex consisting of TANK, IKBKB and IKBKG. Interacts with ZFAND5. Interacts with RIPK2. Interacts with TNIP1 and TNFAIP3; TNIP1 facilitates the TNFAIP3-mediated de-ubiquitination of IKBKG (By similarity). Interacts with TNFAIP3; the interaction is induced by TNF stimulation and by polyubiquitin. Binds polyubiquitin; the interaction is mediated by two domains; reports about the binding to 'Lys-63'-linked and/or linear polyubiquitin, respective binding affinities and stoichiometry are conflicting. Interacts with Shigella flexneri ipah9.8; the interaction promotes TNIP1-dependent 'Lys-27'-linked polyubiquitination of IKBKG which perturbs NF-kappa-B activation during bacterial infection. Interacts with NLRP10. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Sumoylated NEMO accumulates in the nucleus in response to genotoxic stress. Tissue Specificity: Heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney and pancreas. Post-translational modifications: Phosphorylation at Ser-68 attenuates aminoterminal homodimerization. Polyubiquitinated on Lys-285 through 'Lys-63'; the ubiquitination is mediated by NOD2 and RIPK2 and probably plays a role in signaling by facilitating interactions with ubiquitin domain-containing proteins and activates the NF-kappa-B pathway. Polyubiquitinated on Lys-399 through 'Lys-63'; the ubiquitination is mediated by BCL10, MALT1 and TRAF6 and probably plays a role in signaling by facilitating interactions with ubiquitin domain-containing proteins and activates the NF-kappa-B pathway. Monoubiquitinated on Lys-277 and Lys-309; promotes nuclear export. Polyubiquitinated through 'Lys-27' by TRIM23; involved in antiviral innate and inflammatory responses. Linear polyubiquitinated on Lys-111, Lys-143, Lys-226, Lys-246, Lys-264, Lys-277, Lys-285, Lys-292, Lys-302, Lys-309 and Lys-326; the head-to-tail polyubiquitination is mediated by the LUBAC complex and plays a key role in NF-kappa-B activation. Polyubiquitinated on Lys-309 and Lys-321 via 'Lys-27'-linked ubiquitin by Shigella flexneri E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ipah9.8, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Sumoylated on Lys-277 and Lys-309 with SUMO1; the modification results in phosphorylation of Ser-85 by ATM leading to a replacement of the sumoylation by mono-ubiquitination on these residues. Neddylated by TRIM40, resulting in stabilization of NFKBIA and down-regulation of NF-kappa-B activity. DISEASE: Defects in IKBKG are the cause of ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic with immunodeficiency X-linked (EDAID) [MIM:300291]; also known as hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency (HED-ID). Is a form of ectoderma dysplasia, a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. Characterized by absence of sweat glands, sparse scalp hair, rare conical teeth and immunological abnormalities resulting in severe infectious diseases. Defects in IKBKG are the cause of ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic with immunodeficiency-osteopetrosis-lymphedema (OLEDAID) [MIM:300301]. Defects in IKBKG are a cause of immunodeficiency NEMO-related without anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (NEMOID) [MIM:300584]; also called immunodeficiency without anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, isolated immunodeficiency or pure immunodeficiency. Patients manifest immunodeficiency not associated with other abnormalities, and resulting in increased infection susceptibility. Patients suffer from multiple episodes of infectious diseases. Defects in IKBKG are the cause of susceptibility to X-linked familial atypical micobacteriosis type 1 (AMCBX1) [MIM:300636]; also known as X-linked disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection type 1 or X-linked susceptibility to mycobacterial disease type 1. AMCBX1 is the X-linked recessive form of Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD). MSMD is a congenital syndrome resulting in predisposition to clinical disease caused by weakly virulent mycobacterial species, such as bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccines and non-tuberculous, environmental mycobacteria. Patients are also susceptible to the more virulent species Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Defects in IKBKG are the cause of recurrent isolated invasive pneumococcal disease type 2 (IPD2) [MIM:300640]. Recurrent invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) is defined as two episodes of IPD occurring at least 1 month apart, whether caused by the same or different serotypes or strains. Recurrent IPD occurs in at least 2% of patients in most series, making IPD the most important known risk factor for subsequent IPD. Defects in IKBKG are the cause of incontinentia pigmenti (IP) [MIM:308300]; formerly designed familial incontinentia pigmenti type II (IP2). IP is a genodermatosis usually prenatally lethal in males. In affected females, it causes abnormalities of the skin, hair, eyes, nails, teeth, skeleton, heart, and central nervous system. The prominent skin signs occur in four classic cutaneous stages: perinatal inflammatory vesicles, verrucous patches, a distinctive pattern of hyperpigmentation and dermal scarring. Similarity: Contains 1 C2HC-type zinc finger. SWISS: Q9Y6K9 Gene ID: 8517 Database links: Entrez Gene: 8517 Human Entrez Gene: 16151 Mouse Omim: 300248 Human SwissProt: Q9Y6K9 Human SwissProt: O88522 Mouse Unigene: 43505 Human Unigene: 12967 Mouse Unigene: 214715 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |